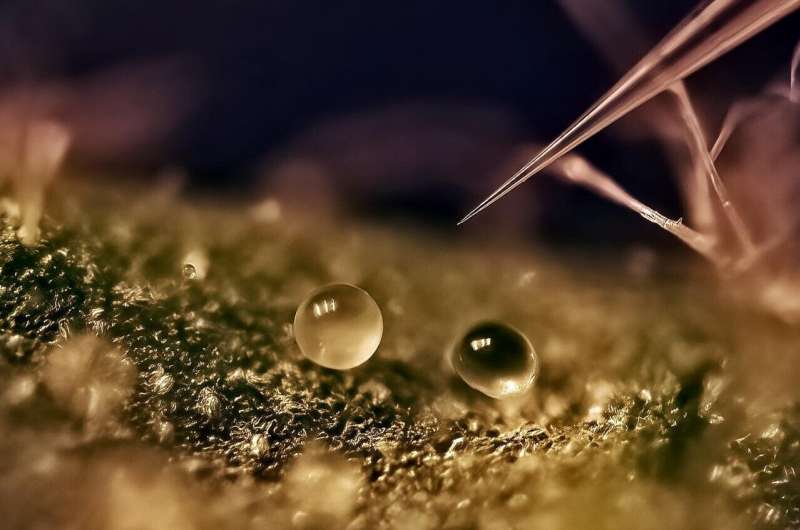
Neural networks and robotic microneedles enable autonomous extraction of plant metabolites.
Credit: Kaare Hartvig Jensen/ http://jensen-research.com/
Physicists from DTU have studied whether valuable chemical substances can be harvested directly from the cells of plants. Using a harvester measuring only a few microns, they have now achieved a technological breakthrough
The goal of Kaare Hartvig Jensen, Associate Professor at DTU Physics, was to reduce the need for harvesting, transporting, and processing crops for the production of biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and other products. The new method of extracting the necessary substances, which are called plant metabolites, also eliminates the need for chemical and mechanical processes.
Plant metabolites consist of a wide range of extremely important chemicals. Many, such as the malaria drug artemisinin, have remarkable therapeutic properties, while others, like natural rubber or biofuel from tree sap, have mechanical properties.
Harvesting cell by cell
Because most plant metabolites are isolated in individual cells, the method of extracting the metabolites is also important, since the procedure affects both product purity and yield.
Usually the extraction involves grinding, centrifugation, and chemical treatment using solvents. This results in considerable pollution, which contributes to the high financial and environmental processing costs.
“All the substances are produced and stored inside individual cells in the plant. That’s where you have to go in if you want the pure material. When you harvest the whole plant or separate the fruit from the branches, you also harvest a whole lot of tissue that doesn’t contain the substance you’re interested in,” explains Kaare Hartvig Jensen.
“So there are two perspectives to it. If you want to extract the pure substances, you need to do it cell by cell. And when you can do that, as we’ve shown, you don’t have to harvest the plant. Then you can put the little robot on and it can work without damaging the plant,” says Kaare.
The team is currently working with plants and leaves, but in the future this type of harvester may be used on a slightly larger scale.
The hope is that this unique approach can create a new source of biomass and spark research into a new area of sustainable energy production.
One thing the technology might be used for in the future is tapping energy from trees, which contain a lot of biofuel.
“In the forests of northern Canada and Russia, there are spruce forests with around 740 billion trees that are completely untouched. That’s about 25% of the total number of trees on the planet. By developing this technology, we can tap trees for sugar and make biofuel without chopping down or damaging the trees,” explains Kaare.
Artificial intelligence at a microscopic level
The cells in the fruit and leaves that the harvester looks for are 100 microns in diameter, and the tip of the needle is around 10 microns in diameter. The harvest is therefore happening on the scale of the width of a hair.
Magnus Valdemar Paludan, the PhD student at DTU Physics who created the system of image analysis, image recognition, and robot control, explains.
“It’s all done with a microscope camera. To begin with, I manually marked pixels on the microscopy images showing the cells that the robot will harvest. That information can be used to train a computer to find similar cells in new images.”
Machine learning and a pre-existing neural network, GoogLeNet, are the building blocks of the technology. The network can already recognize macroscopic structures and can sift through an image and tell you if, for example, there’s an elephant or a red pepper hiding in the photo.
“We used a technique called transfer learning, where you use the existing neural network’s ability to recognize different objects in an image. By showing the computer a number of new images with the manually marked cells, we succeeded in adjusting the network’s parameters so it recognizes the microscopic metabolite-rich cells,” says Magnus.
“The harvester can then go in and take a picture of the leaf with the microscope camera, run it through the software, and recognize the cells it needs to harvest. Next, it can extract the chemicals automatically using a microrobot, while the rest of the plant remains undisturbed,” explains Magnus.
###
The results stem from Kaare Hartvig Jensen’s VILLUM Experiment project, for which he received a grant in 2017. Postdoc Hansol Bae and Jan Knoblauch have also been part of the project.
Facts about VILLUM Experiment
Grants for bold research ideas that are difficult to realize in a classic peer-review funding system.
Awarded for unique research projects that challenge norms and have the potential to fundamentally alter our approach to key questions.
To ensure that researchers have the confidence to submit their most ambitious ideas without being ‘disparaged’ by the peers who will evaluate their research ideas, the applicants are anonymized. This rule was also introduced to reduce possible bias on the part of the evaluators.
The evaluators are asked to highlight the ideas they see as real innovations. Perhaps only one in 10 projects will turn out to create something unique.
Each expert has the opportunity to assign a ‘trump’ card to one application. If this happens, it requires powerful arguments for the foundation’s board to choose not to support the idea.
The granted awarded is DKK 1-2 million, which must cover a research period of 1-2 years.
The programme is open to all researchers of any nationality, and applications are welcome from active researchers of any age.
Original Article: The world’s smallest fruit picker controlled by artificial intelligence
More from: Technical University of Denmark
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Extracting plant metabolites
- Walk Aims To Put People With MS At Center Of Support
Hundreds turned out on Sunday to take the next step in helping to find a cure for Multiple Sclerosis by participating in Walk MS St. Cloud at Apollo High School.
- Choosing the right multivitamin supplement for you
One A Day is available in 15 formulations for everyone from teenage boys to women watching their "metabolism"; its competitor Centrum ... Even if botanical ingredients, food extracts, and other ...
- Everything You Need to Know About Omega-5s
Dietitians explain what omega-5s are, their health benefits, if you need to be taking an omega-5 supplement, and the risks of taking an omega-5 supplement.
- The 11 Best Hair Growth Serums for Long, Strong Hair
First, it helps to understand what’s causing your hair changes. “I encourage everyone with a concern for hair thinning or shedding to consult with a health-care provider first,” says Paradi Mirmirani, ...
- Best organic CBG oil: benefits, side effects, and 4 products we love
Curious about CBG? Learn all you need to know about the cannabinoid and see the best organic CBG oil on the market.
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Extracting plant metabolites
[google_news title=”” keyword=”extracting plant metabolites” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Transfer learning
- The Transfer Portal for Jewish College Students
Every day this week, another college athlete has announced that they are transferring to another school. The “Transfer Portal” can be a powerful tool for athletes seeking better opportunities and ...
- Is it time to be concerned about the transfer portal's impact on Duke men's basketball?
Will the transfer portal hurt or benefit the Blue Devils? The Blue Zone is here to break down both sides of the situation.
- How cognitive and physical demands interact when learning to play the piano
Learning new skills involves intricate brain processes that scientists are still working to fully understand. A recent study published in the journal Brain Sciences examines how older adults learn ...
- Hailey Van Lith finally makes transfer decision after TCU twist
After entering the transfer portal, ex-LSU and Louisville star Hailey Van Lith has officially committed to TCU, she announced on her social media on Friday. “The pen has officially hit the paper,” she ...
- Ranking the top 20 players in college football’s transfer portal this spring
Transfers are ranked based on their experience, production, potential, interest they’re generating and feedback from coaches.
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Transfer learning
[google_news title=”” keyword=”transfer learning” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]