A study led by scientists at The Wistar Institute describes a novel immunotherapeutic strategy for the treatment of cancer based on the use of synthetic DNA to directly encode protective antibodies against a cancer specific protein. This is the first application of the new technology, called DNA-encoded monoclonal antibody (DMAb), for cancer immunotherapy. The study was published online in Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.
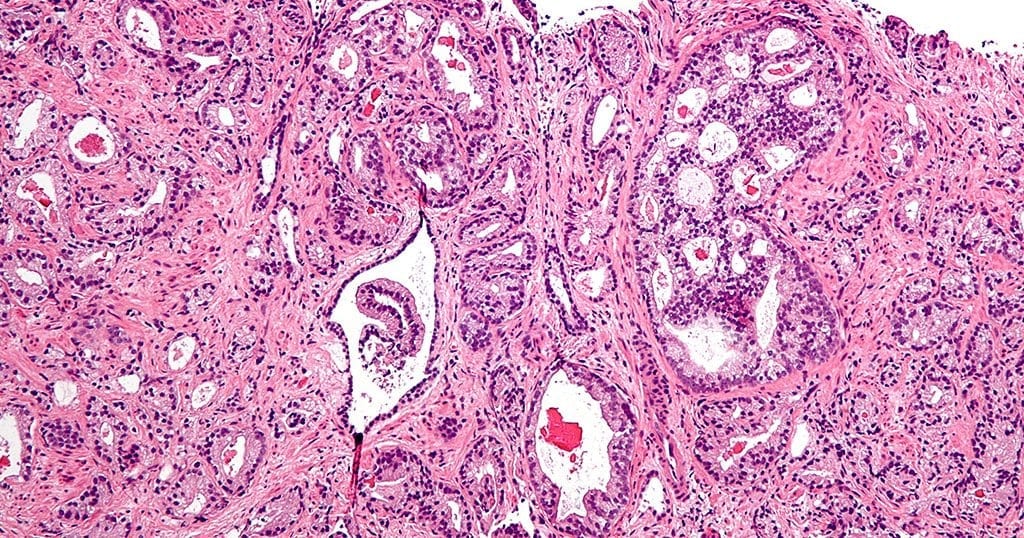
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide. Traditional treatments are invasive and can impair the quality of life of patients, underscoring the need for alternative therapeutic strategies, including immunotherapy. One of the immunotherapeutic approaches that has been explored thus far relies on the use of monoclonal antibodies that specifically target a protein present on the surface of prostate cancer cells called prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) to elicit an anti-tumor immune response and control the cancer. Although promising, this strategy is limited by the production cost required to make these therapeutic antibodies. Additionally, multiple infusions are often required to achieve efficacy.
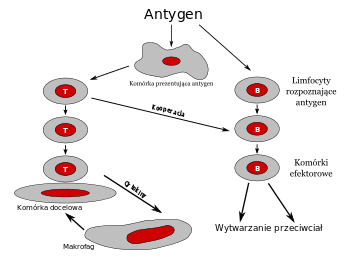
Wistar researchers devised a novel DNA-based approach in which an engineered DNA plasmid is constructed and used to deliver the instructions to make the desired anti-PSMA antibody so that the therapy can be generated in the patient’s body in a sustained manner. This research has important implications for the use of DNA-encoded monoclonal antibody technology as a platform for delivering the next generation of immunotherapies for cancer and many human diseases.
“This is an important demonstration of the possibilities opened up for immunotherapy by DMAb technology to direct in vivoproduction of antibodies of major relevance to human cancer,” said David B. Weiner, Ph.D., executive vice president of The Wistar Institute, director of The Wistar Institute Vaccine & Immunotherapy Center, W.W. Smith Charitable Trust Professor in Cancer Research, and senior author of the study. “There is a great need for such new approaches for prostate disease as well as many other cancers. As recent data suggest, PSMA is an important cancer antigen expressed on many human prostate, bladder, renal as well as ovarian cancers, so additional study of the possible benefits of this therapy are important.”
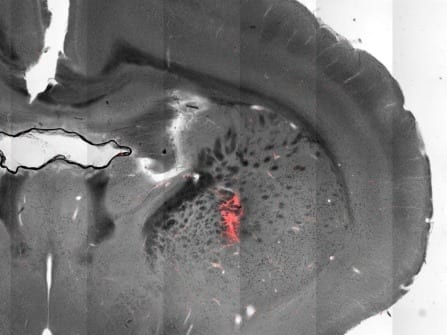
The new technology was tested in mice for the ability to generate antibodies in their blood stream that would target human PSMA as well as target PSMA-positive tumors. Results showed that antibodies were able to bind to the cancer cells and recruited specific immune cells called natural killer cells, resulting in shrinkage of the tumor, significantly improving survival.
“Our data provide proof of concept that DMAb engineered DNA plasmids can be successfully used to target important cancers,” said Kar Muthumani, M.Sc., Ph.D., assistant professor in the Translational Tumor Immunology Program at Wistar, member of the Vaccine & Immunotherapy Center and lead author of the study. “The unique features of our synthetic DNA-based system make it a promising novel approach for cancer therapy, alone or in combination with other treatments.”
Learn more: Wistar Scientists Develop Novel Immunotherapy Technology for Prostate Cancer
The Latest on: Synthetic DNA
[google_news title=”” keyword=”synthetic DNA” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]- Marriage of synthetic biology and 3D printing produces programmable living materialson May 1, 2024 at 6:42 am
Scientists are harnessing cells to make new types of materials that can grow, repair themselves and even respond to their environment. These solid "engineered living materials" are made by embedding ...
- Crafting Programmable Living Materials With Synthetic Biology & 3D Printingon May 1, 2024 at 4:59 am
New study uses 3D printing and genetically modified plant cells to create complex, self-repairing materials that could revolutionize biomanufacturing and construction. Scientists are harnessing cells ...
- JD Sports Moves To DNA Spray To Cut Down Theft Rate Other Retailers Set To Followon April 30, 2024 at 3:42 pm
Retail theft is surging in Australia with CE and small appliance retailers along with department stores investing millions in prevention, some retailers such as JD Sports have moved to use a unique ...
- Scientists construct sophisticated synthetic system using self-replicating nanostructureson April 29, 2024 at 7:03 am
A research team led by the late Professor Liang Haojun from the Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale of University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has developed ...
- Openreach reaps benefit of invisible DNA marking with cable thefts down 30%on April 28, 2024 at 11:45 pm
Despite spate of cable thefts in recent times, Openreach reports crime tumbling over past 12 months after deploying forensic liquid marker that can be sprayed directly onto cables and equipment.
- Applied DNA Awarded Contract by HDT Bio For Rapid Vaccine Development Programon April 25, 2024 at 5:24 am
Under the terms of the contract, Applied DNA will supply Linea™ DNA IVT templates to HDT Bio for use in conjunction with its LION™ formulated repRNA (self-replicating RNA) vaccination platform. The ...
- DNA Synthesis Approaches: Will New Methods Stand The Test Of Time?on April 24, 2024 at 6:00 am
Both chemical and enzymatic synthesis companies need to continue working to overcome their respective hurdles.
- Self-assembling synthetic cells act like living cells with extra abilitieson April 23, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Using DNA and proteins, scientists have created new synthetic cells that act like living cells. Blurring the line between artificial and living materials, these cells can be reprogrammed to perform ...
- A new method for enzymatic synthesis of potential RNA therapeuticson April 23, 2024 at 9:10 am
A team of researchers at IOCB Prague led by Prof. Michal Hocek has developed a novel method for preparing ribonucleic acid (RNA) containing modified bases. Innovative use of engineered DNA polymerases ...
- Applied DNA Announces 1-For-20 Reverse Stock Spliton April 22, 2024 at 12:25 pm
Applied DNA Sciences, Inc. (NASDAQ:APDN) (Applied DNA or the Company), a leader in PCR-based DNA technologies, today announced that it will effect a 1-for-20 stock split of its common stock, to be ...
via Google News and Bing News