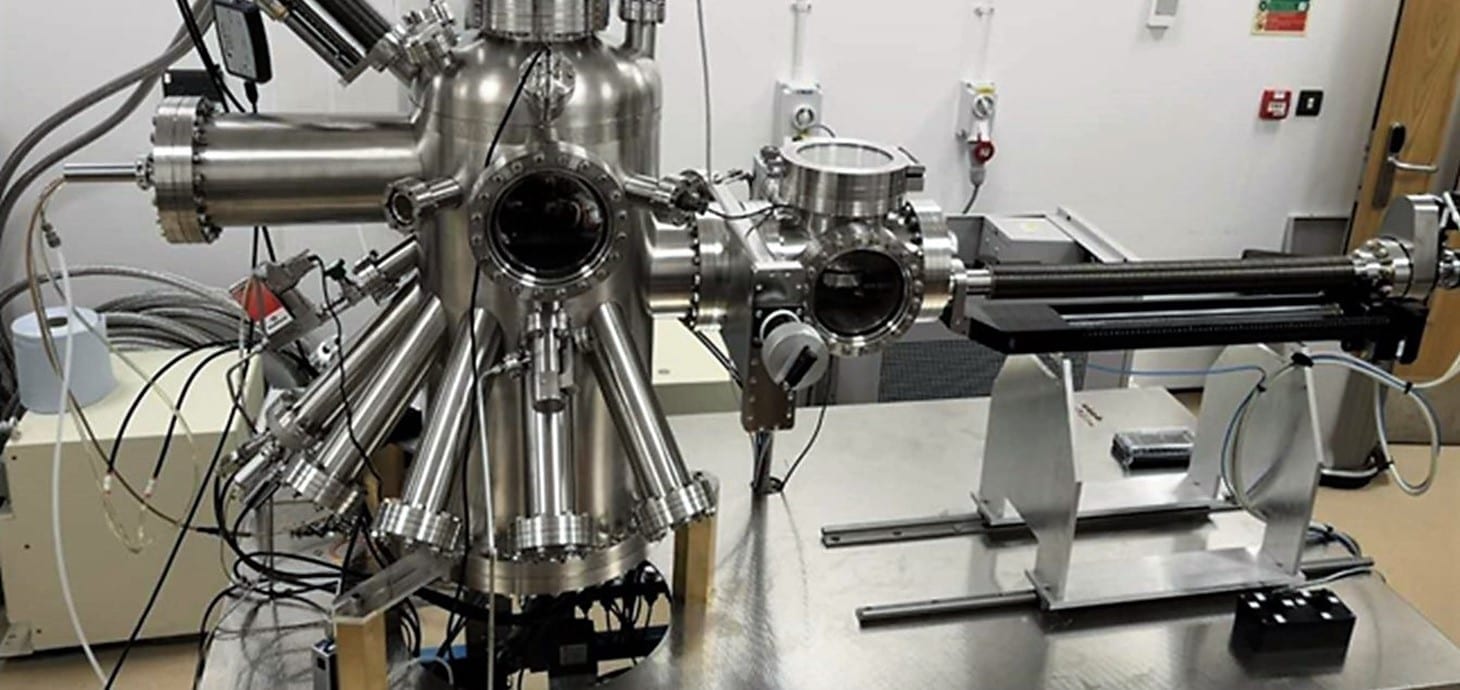
The Matrix Assembly Cluster Source, a newly invented machine used to design a breakthrough water treatment method using a solvent-free approach.
Researchers from Swansea University have developed a new environmentally friendly method for removing toxic chemicals from water.
A newly invented machine, called the Matrix Assembly Cluster Source (MACS), has been used to design a breakthrough water treatment method using a solvent-free approach.
The research, from The Institute for Innovative Materials, Processing and Numerical Technologies (IMPACT) within the College of Engineering at Swansea University, was funded by the EPSRC and led by Professor Richard Palmer.
Professor Richard Palmer explains:
“The harmful organic molecules are destroyed by a powerful oxidising agent, ozone, which is boosted by a catalyst. Usually such catalysts are manufactured by chemical methods using solvents, which creates another problem – how to deal with the effluents from the manufacturing process?
The Swansea innovation is a newly invented machine that manufactures the catalyst by physical methods, involving no solvent, and therefore no effluent. The new technique is a step change in the approach to water treatment and other catalytic processes.”
Professor Palmer continues:
“Our new approach to making catalysts for water treatments uses a physical process which is a vacuum-based and solvent free method. The catalyst particles are clusters of silver atoms, made with the newly invented MACS machine.
It solves the longstanding problem of low cluster production rate – meaning, for the first time, it is now possible to produce enough clusters for study at the test tube level, with the potential to then scale up further to the level of small batch manufacturing and beyond.”
The clusters are approximately 10,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair and have been of significant interest to researchers because of their unique properties. However, due to the inadequate rate of cluster production, research in this area has been limited.
The new MACS method has changed this – it scales up the intensity of the cluster beam to produce enough grams of cluster powder for practical testing. The addition of ozone to the powder then destroys pollutant chemicals from water, in this case nitrophenol.
On the future potential of this breakthrough technology, Professor Palmer summarises:
“The MACS approach to the nanoscale design of functional materials opens up completely new horizons across a wide range of disciplines – from physics and chemistry to biology and engineering. Thus, it has the power to enable radical advances in advanced technology – catalysts, biosensors, materials for renewable energy generation and storage.
It seems highly appropriate that the first practical demonstration of Swansea’s environmentally friendly manufacturing process concerns something we are all concerned about – clean water!”
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Removing toxic chemicals from water
- Treating Tampa Bay’s “Forever Chemicals” in Our Drinking Water
The EPA has recently set limits on PFAS hazardous "forever chemicals" in our drinking water supply. Find out from our local water quality experts how our water utilities plan to remove PFAS from our ...
- Breaking Down New Rules About ‘Forever Chemicals’
Lisa Friedman, who covers climate change, discussed the fight to regulate toxic chemicals found in nearly half of America’s tap water.
- With new 'forever chemical' standards set, how will NC utilities clean up their water?
Filtering manmade chemicals like GenX out of public water supplies could cost billions. Utilities say customers shouldn't have to shoulder the costs.
- What you need to know about toxic “forever chemicals” the EPA is restricting
The EPA recently set new limits on the toxic chemicals used to make everything from nonstick pans to firefighting foam. Here’s how to protect yourself and your family.
- Biden’s New Regulation Will Limit Toxic Chemicals In Drinking Water Across The Country
President Joe Biden’s administration announced the first-ever national limits on toxic “forever chemicals” in drinking water. This plan will require utilities serving roughly one in three Americans to ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Removing toxic chemicals from water
[google_news title=”” keyword=”removing toxic chemicals from water” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Matrix Assembly Cluster Source
- The Matrix Is Getting a Fifth Movie—Without a Wachowski Directing
Saying the quiet part out loud. Somehow, this has always felt like the bleeding heart of The Matrix movies. Under the simulation theory, cool bullet-dodging, and even cooler soundtracks ...
- ‘The Matrix 5’ is officially in the works with a new director
Carrie-Anne Moss and Keanu Reeves in the 1999 movie 'The Matrix' CREDIT: Getty/Photo by Ronald Siemoneit/Sygma/Sygma via Getty Images Warner Bros. has announced that a fifth instalment of The ...
- The Matrix is coming back for a fifth movie
“It is not hyperbole to say The Matrix films changed both cinema and my life,” Goddard said. “Lana and Lilly’s exquisite artistry inspires me on a daily basis, and I am beyond grateful for ...
- The Matrix 5 Is A Go With A Major Behind The Scenes Change, And I'm Conflicted On How To Feel About This News
This year marks the 25th anniversary of that time Lana and Lilly Wachowski blew the minds of the world by showing us what The Matrix truly was. Still considered one of the best sci-fi movies of ...
- Everything you need to know about The Matrix 5
That could have been the franchise’s final chapter, but Warner Bros. has announced that a fifth Matrix film is going forward. To bring everyone up to speed, here’s everything you need to know ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Matrix Assembly Cluster Source
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Matrix Assembly Cluster Source” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]