via La Trobe University
A team of scientists from La Trobe University has shown a protein found in a tobacco plant has the potential to fight life-threatening infectious diseases
The scientific discovery, published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications could lead to the development of a new class of antibiotics and meet the challenge of rising antibiotic resistance.
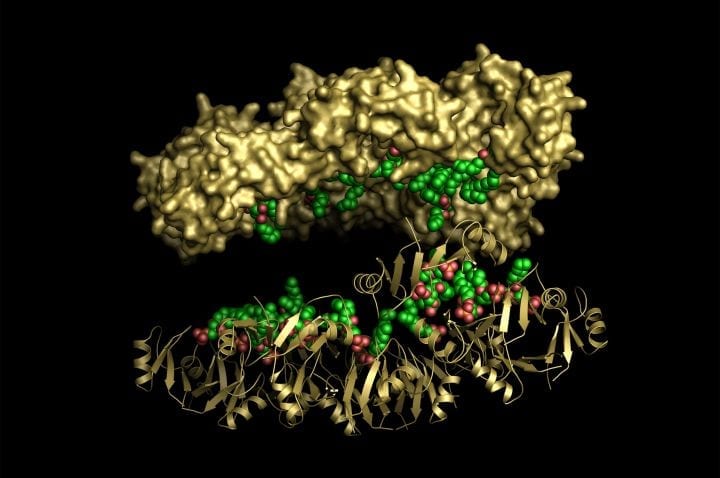
Dr Mark Hulett and Dr Marc Kvansakul from the La Trobe Institute for Molecular Science said their team had demonstrated the peptide NaD1 found in the flowers of the ornamental tobacco plant Nicotiana alata has infection-busting qualities.
“Infectious diseases are a major global health problem, accounting for more than one in eight deaths and mortality rates are predicted to skyrocket over the next 30 years,” Dr Hulett said.
“Antibiotic resistance at the current rate will eventually lead to the exhaustion of effective long-term drug options. It’s imperative we develop new antibiotic treatments.”
Using the power of the Australian Synchrotron, the team led by Dr Hulett and Dr Kvansakul have shown in atomic detail how the tobacco plant peptide can target and destroy the micro-organism responsible for a dangerous fungal infection.
The peptide perforates the parachute-like outer layer of Candida albicans cells, ripping them apart and causing them to explode and die.
“They act in a different way to existing antibiotics and allow us to explore new ways of fighting infections.
“It’s an exciting discovery that could be harnessed to develop a new class of life-saving antimicrobial therapy to treat a range of infectious diseases, including multi-drug-resistant golden staph, and viral infections such as HIV, Zika virus, Dengue and Murray River Encephalitis.”
In 2014, Dr Hulett and Dr Kvansakul found NaD1 could also be effective in killing cancer cells.
Background
Candida albicans is responsible for life-threatening infections in immune-compromised patients, including those diagnosed with cancer and transplant recipients. There are limited effective antibiotics available to treat the infection.
Nicotiana alata flowers naturally produce potent anti-fungal molecules for protection against disease. The plant is related, but different, to tobacco plants grown for commercial use.
Learn more: La Trobe’s infection-busting discovery
The Latest on: Antimicrobial therapy
[google_news title=”” keyword=”antimicrobial therapy” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Antimicrobial therapy
- Carbapenem use in US hospitals: guidance and stewardshipon April 25, 2024 at 4:12 pm
The incidence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales infections has increased substantially in recent years, now accounting for approximately 15% of isolates causing infections.1 ...
- Study: Antibiotic use in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 appears to have no beneficial effect on clinical outcomeson April 25, 2024 at 3:10 pm
Antibiotic treatment of adults hospitalized with moderate COVID-19 is associated with clinical deterioration, despite the drugs being given to over 40% of patients, according to new research being ...
- Researchers systematically investigate efficacy of CRISPR antimicrobial agentson April 25, 2024 at 1:28 pm
The antimicrobial potential of CRISPR-Cas systems is promising, yet how to best design or implement CRISPR nucleases remains poorly understood. An international team led by the Helmholtz Institute for ...
- FDA approves Utility’s Pivya to treat urinary tract infectionson April 25, 2024 at 3:12 am
And the endorsement has come for an oral antibiotic that has been available in Europe for more than 40 years. It’s an odd set of circumstances and a dose of foresight by Utility Therapeutics that ...
- F.D.A. Approves Antibiotic for Increasingly Hard-to-Treat Urinary Tract Infectionson April 24, 2024 at 1:45 pm
Pivmecillinam, which has been used in Europe for decades, will become available next year to women 18 and older.
- Travelers' Diarrhea: Antimicrobial Therapy and Chemopreventionon April 23, 2024 at 5:00 pm
because a single agent might be appropriate for therapy of diarrhea, respiratory and bacterial urinary tract infections. The travelers' diarrhea studies by the author that are reported herein have ...
- Travelers' Diarrhea: Antimicrobial Therapy and Chemopreventionon April 23, 2024 at 5:00 pm
The advice given is to allow the traveler to determine when to initiate therapy based on how they feel. Many debilitating enteric illnesses are associated with excessive abdominal complaints ...
- Cohort study of patients with advanced cancer: outcomes associated with duration of antibiotic therapy for non-ventilator hospital-acquired pneumoniaon April 18, 2024 at 4:50 am
Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA Section of Infectious Diseases, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA ...
- Irish team develops therapy for deadly sepsis crisison April 17, 2024 at 9:00 pm
Inthelia Therapeutics, founded by two top Irish scientists, is switching focus to block infection getting a grip on patients in the first place ...
via Bing News