It could be used cosmetically within three years
Scientists in Japan have created a microscopically thin film that can coat individual teeth to prevent decay or to make them appear whiter, the chief researcher said.
The “tooth patch” is a hard-wearing and ultra-flexible material made from hydroxyapatite, the main mineral in tooth enamel, that could also mean an end to sensitive teeth.
“This is the world’s first flexible apatite sheet, which we hope to use to protect teeth or repair damaged enamel,” said Shigeki Hontsu, professor at Kinki University’s Faculty of Biology-Oriented Science and Technology in western Japan.
“Dentists used to think an all-apatite sheet was just a dream, but we are aiming to create artificial enamel,” the outermost layer of a tooth, he said earlier this month.
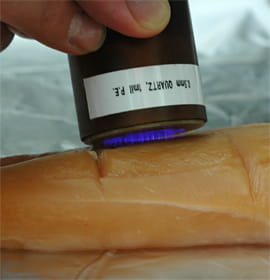
Researchers can create film just 0.004 millimetres (0.00016 inches) thick by firing lasers at compressed blocks of hydroxyapatite in a vacuum to make individual particles pop out.
These particles fall onto a block of salt which is heated to crystallise them, before the salt stand is dissolved in water.
The film is scooped up onto filter paper and dried, after which it is robust enough to be picked up by a pair of tweezers.
“The moment you put it on a tooth surface, it becomes invisible. You can barely see it if you examine it under a light,” Hontsu told AFP by telephone.
The sheet has a number of minute holes that allow liquid and air to escape from underneath to prevent their forming bubbles when it is applied onto a tooth.
via The Raw Story
The Latest Streaming News: Tooth decay updated minute-by-minute
Bookmark this page and come back often
Latest NEWS
Latest VIDEO