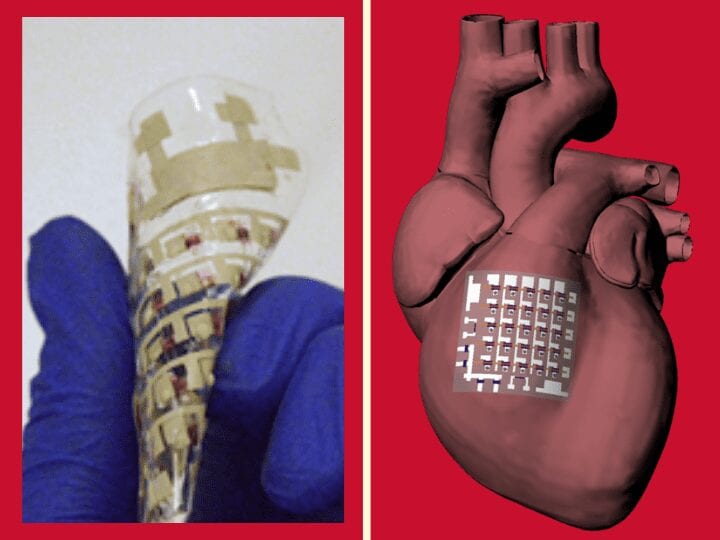
Cunjiang Yu, Bill D. Cook Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at UH, led a group of researchers that developed a cardiac patch made from fully rubbery electronics that can be placed directly on the heart to collect electrophysiological activity, temperature, heartbeat and other indicators, all at the same time.
Pacemakers and other implantable cardiac devices used to monitor and treat arrhythmias and other heart problems have generally had one of two drawbacks – they are made with rigid materials that can’t move to accommodate a beating heart, or they are made from soft materials that can collect only a limited amount of information.
Researchers led by a mechanical engineer from the University of Houston have reported in Nature Electronics a patch made from fully rubbery electronics that can be placed directly on the heart to collect electrophysiological activity, temperature, heartbeat and other indicators, all at the same time.
Cunjiang Yu, Bill D. Cook Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at UH and corresponding author for the paper, said the device marks the first time bioelectronics have been developed based on fully rubbery electronic materials that are compatible with heart tissue, allowing the device to solve the limitations of previous cardiac implants, which are mainly made out of rigid electronic materials.
“For people who have heart arrhythmia or a heart attack, you need to quickly identify the problem,” Yu said. “This device can do that.” Yu is also a principle investigator with the Texas Center for Superconductivity at UH.
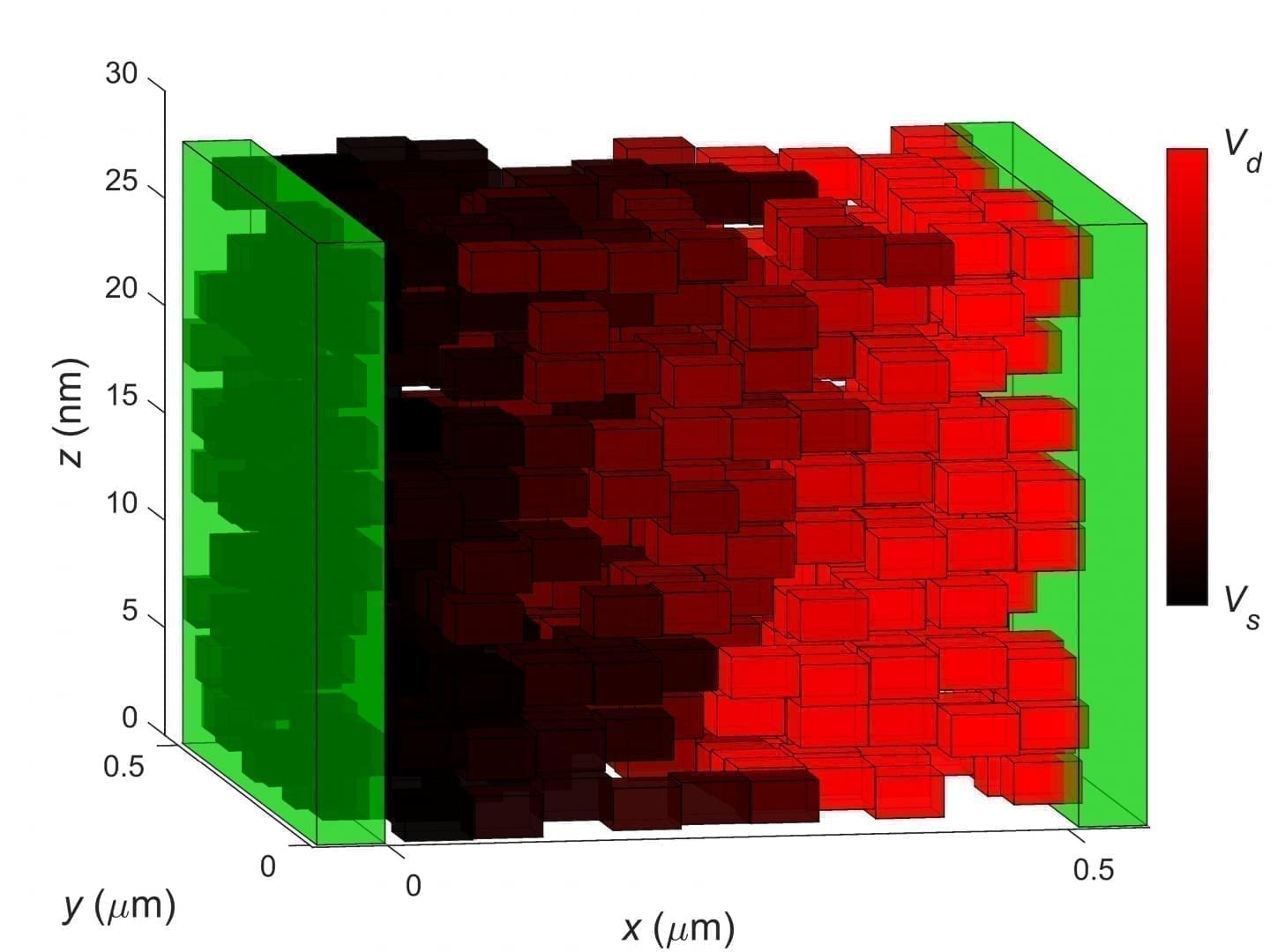
In addition to the ability to simultaneously collect information from multiple locations on the heart – a characteristic known as spatiotemporal mapping – the device can harvest energy from the heart beating, allowing it to perform without an external power source. That allows it to not just track data for diagnostics and monitoring but to also offer therapeutic benefits such as electrical pacing and thermal ablation, the researchers reported.
Yu is a leader in the development of fully rubbery electronics with sensing and other biological capabilities, including for use in robotic hands, skins and other devices. The epicardial bioelectronics patch builds upon that with a material with mechanical properties that mimic cardiac tissue, allowing for a closer interface and reducing the risk that the implant could damage the heart muscle.
“Unlike bioelectronics primarily based on rigid materials with mechanical structures that are stretchable on the macroscopic level, constructing bioelectronics out of materials with moduli matching those of the biological tissues suggests a promising route towards next-generational bioelectronics and biosensors that do not have a hard–soft interface for the heart and other organs,” the researchers wrote. “Our rubbery epicardial patch is capable of multiplexed ECG mapping, strain and temperature sensing, electrical pacing, thermal ablation and energy harvesting functions.”
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Rubbery bioelectronics
- Rubber industry in Thailand - statistics & facts
Rubber cultivation was first introduced in the early 1900s in the southern region of Thailand. The cultivation of rubber trees in Thailand had since then become widely practiced due to the highly ...
- How to Clean Sticky Rubber So It's Good as New
Whether it's golf club grips, electronic objects, kitchen stuff, or the soles of your shoes, rubber shows up a lot in our daily life. So when it gets sticky, it gets icky. Feel free to quote us on ...
- Understanding Bioelectronics: The Intersection of Biology and Electronics
Definition: Bioelectronics is an interdisciplinary field that blends biology with electronics, focusing on the development and application of electronic devices and technologies to biology and ...
- RUBBER: Reform
The International Rubber Regulation Committee, with almost nothing left to regulate, last week decided on a new course — cooperation. IRRC’s life expired on Dec. 31. But the Committee ...
- How to Cook Shrimp So They’re Juicy, Not Rubbery
Undercook and they’ll be mushy and translucent; overcook and they’ll be rubbery and nearly inedible. The best way to tell when shrimp are cooked through is to look for visual cues ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Rubbery bioelectronics
[google_news title=”” keyword=”rubbery bioelectronics” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Rubbery electronics
- Cleveland Cavaliers and Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company Unveil New Fab Lab at East Technical High School
The Cleveland Cavaliers and Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company unveiled a newly designed Fab Lab at East Tech High School, in partnership with Cleveland Metropolitan School District (CMSD) on Wednesday, ...
- Kumho targets micro-mobility for NPT
When it comes to the development of nonpneumatic tires, Kumho believes in starting small. Micro, even. That's why the South Korean tire maker is targeting micro-mobility in for the commercialization ...
- $10.3 million in grants for waste and recycling projects announced
Gov. Andy Beshear has announced a series of grants to local governments and universities for projects totaling more than $10.3 million for projects that include recycling, ...
- Silicon Rubber Heating Elements Market Future Revenues to Take Flight as Market Size Continues to Expand
The global silicon rubber heating elements market size was US$ 141.1 million in 2021. The global silicon rubber heating elements market is forecast to grow to US$ 221 million by 2030 by registering a ...
- The Best White Sneakers
But senior style editor Jennifer Hunter, who lives in less-walkable Los Angeles, says that the rubber on hers didn’t start peeling until year seven of light wear. Converse Chuck Taylor All Star ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Rubbery electronics
[google_news title=”” keyword=”rubbery electronics” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]