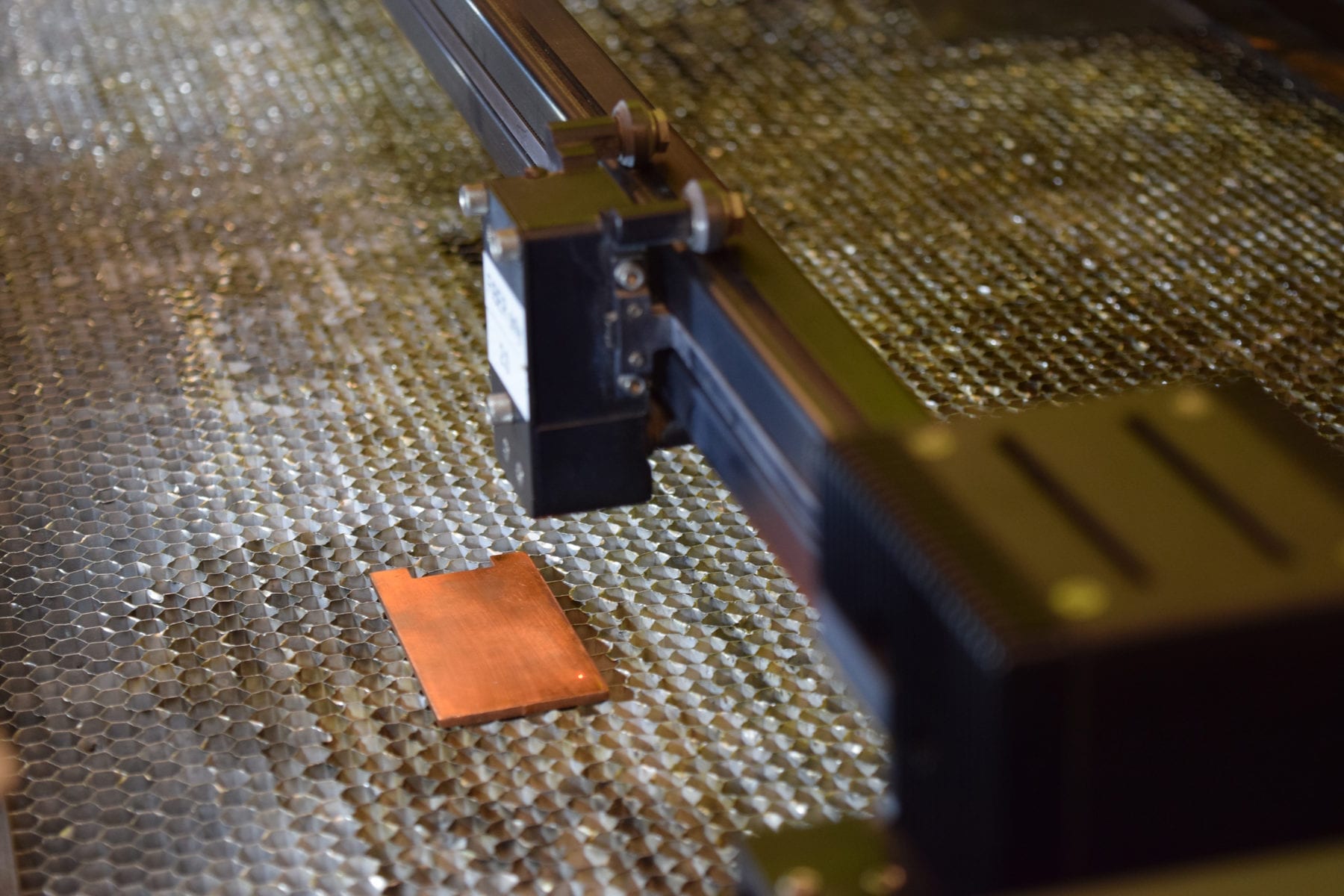
A laser prepares to texture the surface of copper, enhancing its antimicrobial properties. (Purdue University photo/Kayla Wiles)
Bacterial pathogens can live on surfaces for days. What if frequently touched surfaces such as doorknobs could instantly kill them off?
Purdue University engineers have created a laser treatment method that could potentially turn any metal surface into a rapid bacteria killer – just by giving the metal’s surface a different texture.
In a study published in the journal Advanced Materials Interfaces, the researchers demonstrated that this technique allows the surface of copper to immediately kill off superbugs such as MRSA.
“Copper has been used as an antimicrobial material for centuries. But it typically takes hours for native copper surfaces to kill off bacteria,” said Rahim Rahimi, a Purdue assistant professor of materials engineering.
“We developed a one-step laser-texturing technique that effectively enhances the bacteria-killing properties of copper’s surface.”
The technique is not yet tailored to killing viruses such as the one responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, which are much smaller than bacteria.
Since publishing this work, however, Rahimi’s team has begun testing this technology on the surfaces of other metals and polymers that are used to reduce risks of bacterial growth and biofilm formation on devices such as orthopedic implants or wearable patches for chronic wounds.
Giving implants an antimicrobial surface would prevent the spread of infection and antibiotic resistance, Rahimi said, because there wouldn’t be a need for antibiotics to kill off bacteria from an implant’s surface.
The technique might apply to metallic alloys that also are known to have antimicrobial properties.
Metals such as copper normally have a really smooth surface, which makes it difficult for the metal to kill bacteria by contact.
The technique developed by Rahimi’s team uses a laser to create nanoscale patterns on the metal’s surface. The patterns produce a rugged texture that increases surface area, allowing more opportunity for bacteria to hit the surface and rupture on the spot.
Researchers in the past have used various nanomaterial coatings to enhance the antimicrobial properties of metal surfaces, but these coatings are prone to leach off and can be toxic to the environment.
“We’ve created a robust process that selectively generates micron and nanoscale patterns directly onto the targeted surface without altering the bulk of the copper material,” said Rahimi, whose lab develops innovative materials and biomedical devices to address health care challenges.
The laser-texturing has a dual effect: The technique not only improves direct contact, but also makes a surface more hydrophilic. For orthopedic implants, such a surface allows bone cells to more strongly attach, improving how well the implant integrates with bone. Rahimi’s team observed this effect with fibroblast cells.
Due to the simplicity and scalability of the technique, the researchers believe that it could easily be translated into existing medical device manufacturing processes.
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Laser-texturing
- GF Machining Solutions names new managing director
GF Machining Solutions has promoted Onik Bhattacharyya to the position of managing director and head of market region for North and Central Americas. The company said that in his new position, ...
- Should you buy a laser TV? A case for and against laser projectors
There’s another type of display that's been gaining steam, too, though: the laser TV. There are plenty of benefits to a laser TV — like the fact that they support much larger display areas at ...
- Laser light makes a material magnetic
Pulses of laser light can cause any material – including insulators – to develop a relatively large magnetic moment. This effect, which has been demonstrated for the first time by an international ...
- 4 of the Best Home Laser Hair Removal Devices by Hair Color, Coarseness, and More
Here’s our process. You used to have to visit a dermatologist for laser hair removal, and this is still the most effective route, but you can consider home laser hair removal devices instead.
- Best laser printers of 2024
Looking for the best laser printers? Our team of reviewers tested out top models from Xerox, Brother, Lexmark, and more to find out which are worth taking up office space. If you print a lot of ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Laser-texturing
[google_news title=”” keyword=”laser-texturing” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Anti-bacterial surface
- Freshness matters: Study finds newer honey packs a stronger antibacterial punch
Researchers reveal that the antibacterial potency of Hungarian honeys, including their effectiveness against respiratory pathogens, declines with storage time, emphasizing the need for fresh sources ...
- Method Anti Bacterial 2L Refill
Say goodbye to germs with Method antibacterial 2L refill. Formulated to kill 99.9% of bacteria, this plant-based antibacterial solution is tough on germs but gentle on the planet. With biodegradable ...
- 10 Times You Shouldn’t Use Antibacterial Wipes
When you wipe a surface with an antibacterial wipe, you see a gratifying smudge of grime on the white rag. What you don’t see is what’s left behind—chemicals. “The major reason that I believe people ...
- The surface cleaners that really work
On the surface of it, you’d think there might not be much difference between household cleaners. But it is our household surfaces themselves that prove there ...
- The surprising health benefits of dirt
If you’re the kind of person who carries hand sanitiser at all times and thinks cleaning the kitchen means blasting every surface with antibacterial spray, you may want to put down that bottle of ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Anti-bacterial surface
[google_news title=”” keyword=”anti-bacterial surface” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]