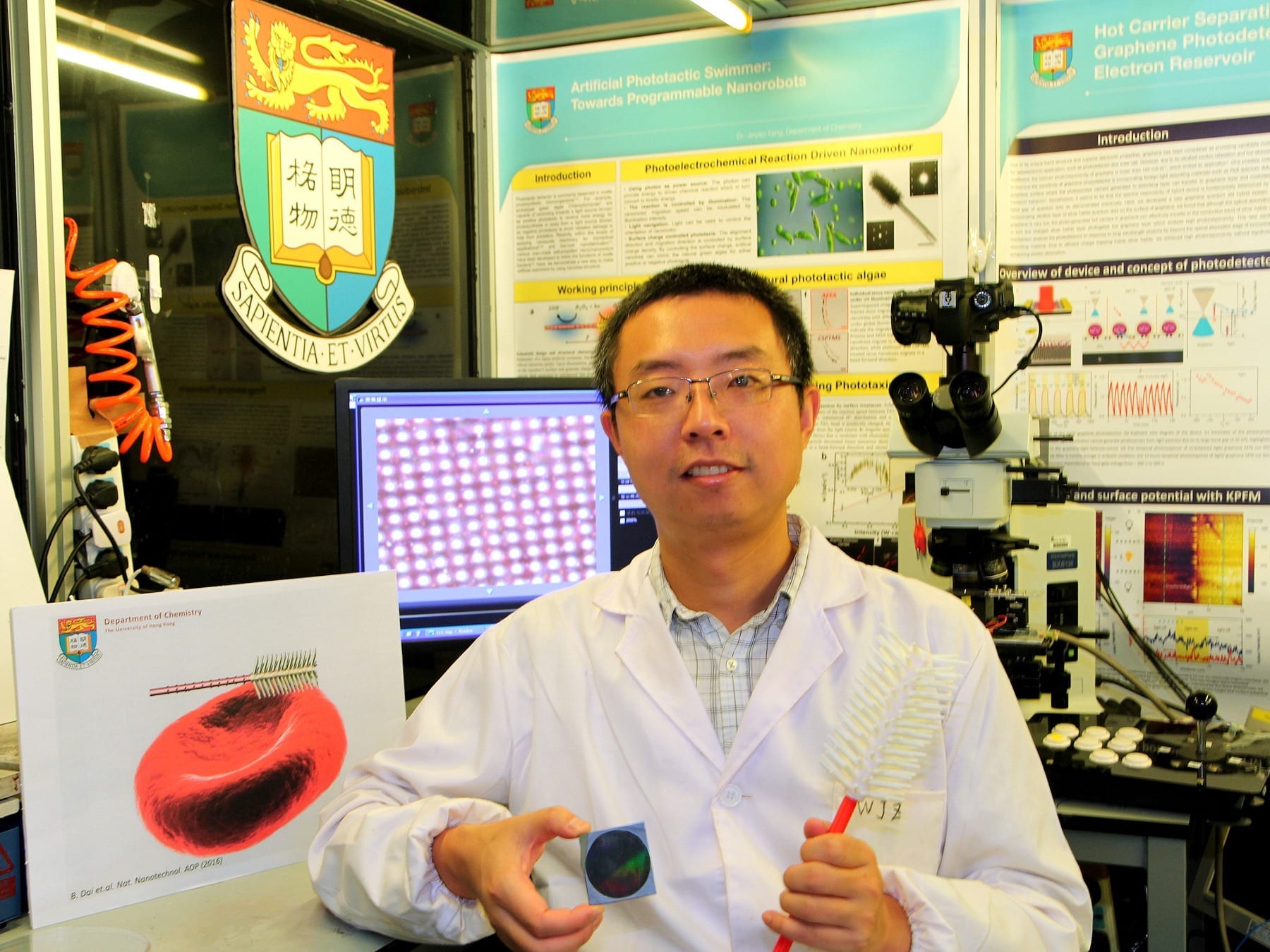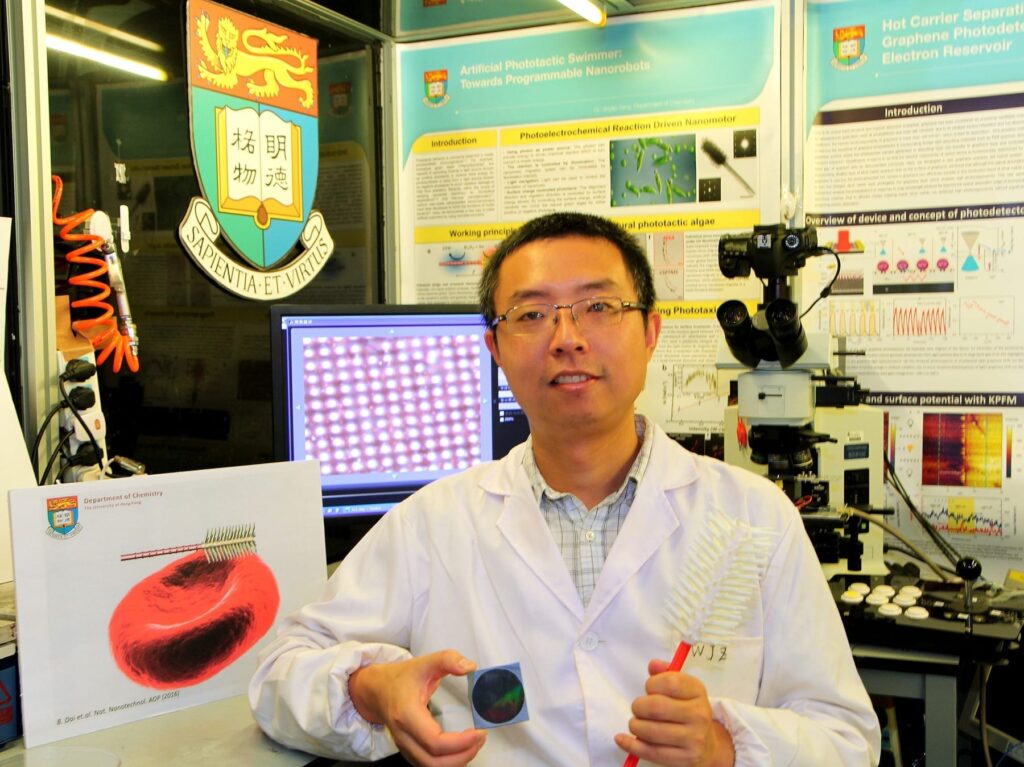
A team of researchers led by Dr Jinyao Tang of the Department of Chemistry, the University of Hong Kong, has developed the world’s first light-seeking synthetic Nano robot. With size comparable to a blood cell, those tiny robots have the potential to be injected into patients’ bodies, helping surgeons to remove tumors and enabling more precise engineering of targeted medications.
The findings have been published in October earlier in leading scientific journal Nature Nanotechnology.
It has been a dream in science fiction for decades that tiny robots can fundamentally change our daily life. The famous science fiction movie “Fantastic Voyage” is a very good example, with a group of scientists driving their miniaturized Nano-submarine inside human body to repair a damaged brain. In the film “Terminator 2”, billions of Nanorobots were assembled into the amazing shapeshifting body: the T-1000. In the real world, it is quite challenging to make and design a sophisticated Nano robot with advanced functions.
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2016 was awarded to three scientists for “the design and synthesis of molecular machines”. They developed a set of mechanical components at molecular scale which may be assembled into more complicated Nano machines to manipulate single molecule such as DNA or proteins in the future. The development of tiny nanoscale machines for biomedical applications has been a major trend of scientific research in recent years. Any breakthroughs will potentially open the door to new knowledge and treatments of diseases and development of new drugs.
One difficulty in Nanorobot design is to make these nanostructures sense and respond to the environment. Given each Nanorobot is only a few micrometer in size which is ~50 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair, it is very difficult to squeeze normal electronic sensors and circuits into Nanorobots with reasonable price. Currently, the only method to remotely control Nanorobots is to incorporate tiny magnetic inside the Nanorobot and guide the motion via external magnetic field.
The Nanorobot developed by Dr Tang’s team use light as the propelling force, and is the first research team globally to explore the light-guided Nanorobot and demonstrate its feasibility and effectiveness. In their paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, Dr Tang’s team demonstrated the unprecedented ability of these light-controlled Nanorobots as they are “dancing” or even spell a word under light control. With a novel Nanotree structure, the Nanorobots can respond to the light shining on it like moths being drawn to flames. Dr Tang described the motions as if “they can “see” the light and drive itself towards it”.
The team gained inspiration from natural green algae for the Nanorobot design. In nature, some green algae have evolved with the ability of sensing light around it. Even just a single cell, these green algae can sense the intensity of light and swim towards the light source for photosynthesis. Dr Jinyao Tang’s team spent three years to successfully develop the Nanorobots. With a novel Nanotree structure, they are composed of two common and low-price semiconductor materials: silicon and titanium oxide. During the synthesis, silicon and titanium oxide are shaped into nanowire and then further arranged into a tiny Nanotree heterostructure.
Dr Tang said: “Although the current Nanorobot cannot be used for disease treatment yet, we are working on the next generation nanorobotic system which is more efficient and biocompatible.”
“Light is a more effective option to communicate between microscopic world and macroscopic world. We can conceive that more complicated instructions can be sent to Nanorobots which provide scientists with a new tool to further develop more functions into Nanorobot and get us one step closer to daily life applications,” he added.
Learn more: HKU chemists develop world’s first light-seeking synthetic Nanorobot for potential biomedical applications
The Latest on: Light-seeking synthetic nanorobots
[google_news title=”” keyword=”light-seeking synthetic nanorobots” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Light-seeking synthetic nanorobots
- Soybeans: Light At The End Of The Tunnelon May 6, 2024 at 3:28 pm
I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock ...
- Showcasing Seeking Alpha's April 2024 New Analystson May 6, 2024 at 12:15 pm
Eighteen new analysts joined us in April, with two of them receiving Editors' Picks on their first publication. We've got folks joining with over two decades of investment experience, including a ...
- Why You May Soon Be Drinking Synthetic Coffeeon May 3, 2024 at 5:01 pm
Your typical morning cup of coffee is a social and environmental disaster—but you’ll soon have the option to start sipping something less harmful: synthetic coffee. Worldwide, people consume ...
- Unleashing the Power of Synthetic Dimensions Revolutionizing Light Manipulationon March 20, 2024 at 3:14 am
Recently, an international team of researchers has made significant strides in manipulating light within synthetic modal dimensions, showcasing the potential for transformative applications in ...
- strobe lighton February 24, 2020 at 4:00 pm
When we last saw [isaac879]’s levitating RGB time fountain, it was made of wood which meant that it would absorb water and didn’t really show off the effect very well. His new version solves ...
- Killer Nanorobots Are Coming For Your Canceron July 31, 2018 at 8:13 pm
At this important stage, that means seeking out the right companies ... is its role in the development of really cool stuff like nanorobots. Illumina shares have performed well, rising 25.6% ...
- Sensation-Seekingon November 11, 2017 at 10:25 pm
Sensation-Seeking: #N# What Is Sensation-Seeking?#N# #N#
- light graffition February 8, 2014 at 4:00 pm
Here’s a quick tip to extend the usefulness of your multimeter. It’s a set of mini test hooks soldered to alligator clips with a short hunk of stranded wire in between. You can buy mini test ...
via Bing News