Copyright : Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA
A new invention uses ionized gas in fluorescent light tubes to transmit Internet wireless frequency signals throughout a building with the aid of already existing electrical wiring.
Due to continuously evolving applications, the electronic communications industry requires high performance and speed efficient systems. However, the physical limitations of microwave devices limits further improvements in current technology. This predicament has led to growing interest in the use of plasma as a conductive element in microwave devices due to their unique and innovative properties, which corresponds with traditional metallic antennas.
Matter exists in four different states: solid, liquid, gas and plasma. Plasma is a type of gas in which the atoms are ionized – they have both free negatively charged electrons and positively charged ions. These charged particles can be controlled by electromagnetic fields, allowing plasmas to be used as a controllable reactive gas.
This invention employs an ionized gas enclosed in a tube as the conducting element of an antenna. When the gas is electrically charged or ionized to plasma, it becomes conductive and allows radio frequency signals to be transmitted or received. When the gas is not ionized, the antenna element ceases to exit.
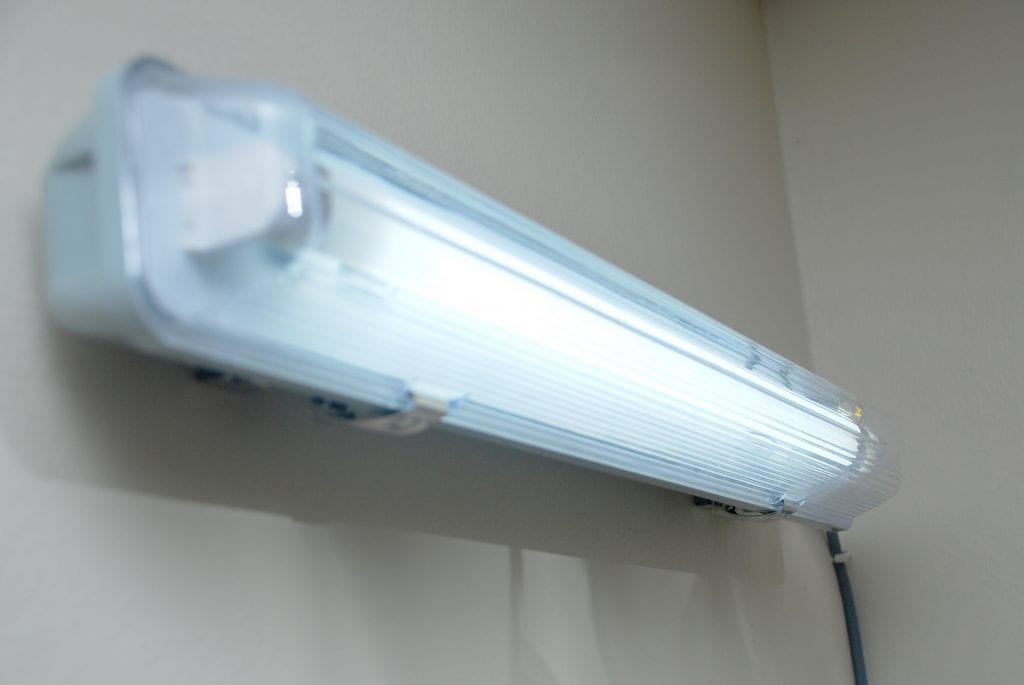
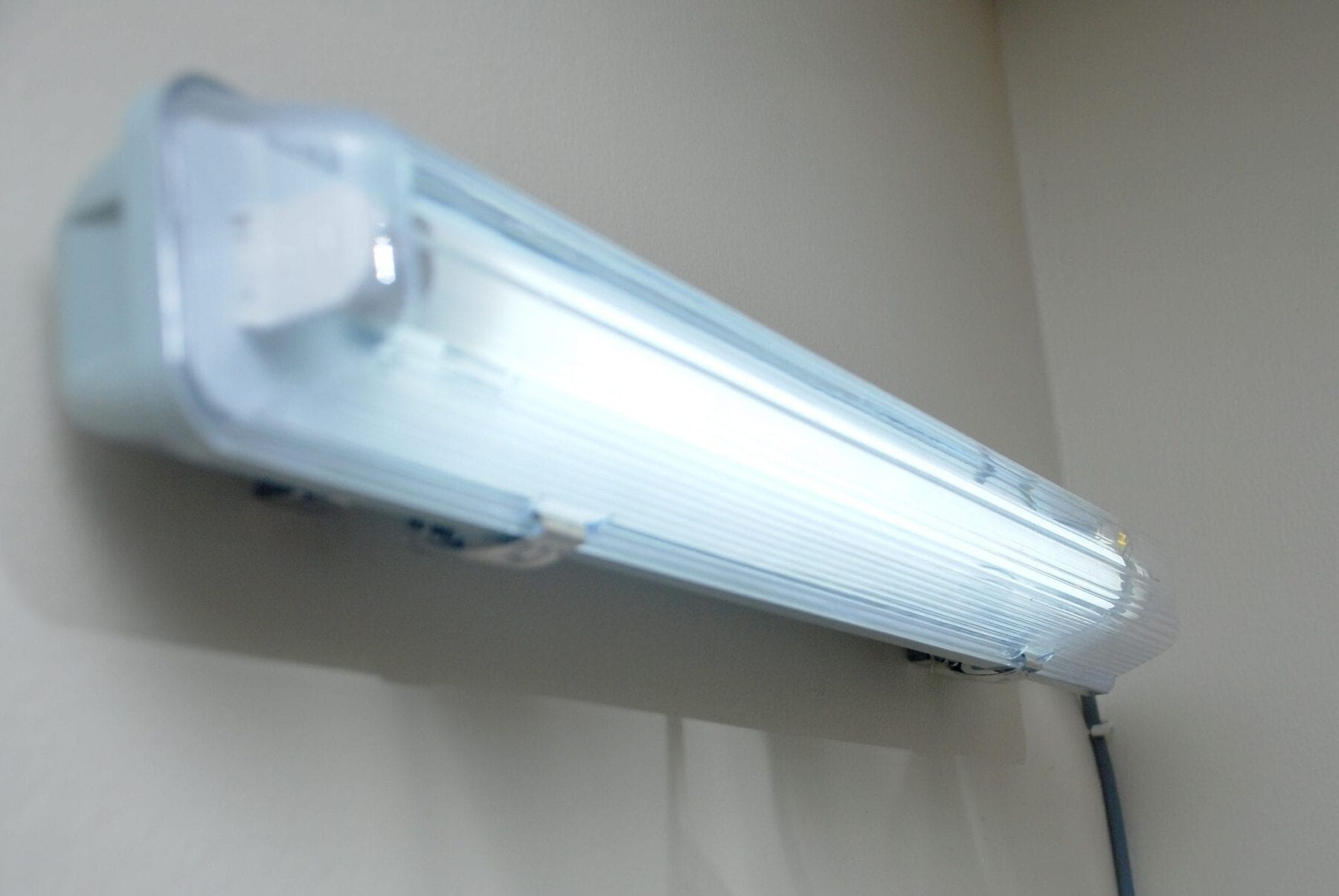
The invention features a smart fluorescent antenna with a 3G/3.75G/4G router for Wi-Fi applications. The antenna operates at the 2.4 GHz frequency band, which is suitable for Wi-Fi applications. A commercially available fluorescent tube, measuring 0.61 metres in length by 0.25 metres in diameter, is used as the plasma antenna. The gas inside the tube is a mixture of argon and mercury vapour, in the ratio 9:1. The tube is energized by a 240 V current, provided by a standard AC power supply. A glowing tube indicates that the gas inside the tube has been ionized to plasma and forms a plasma column. In this state, the plasma column becomes highly conductive and can be used as an antenna.
A coupling sleeve is positioned at the lower end of the tube, which is used to connect the plasma tube to the router. The function of the coupling sleeves is to store the electrical charge. When the gas inside the tube is sufficiently ionized into a plasma state, it becomes conductive and allows radio frequency signals to be transmitted or received.
Measurements indicate that the plasma antenna yields a return loss over 10 dB in the 2.23 GHz to 2.58 GHz frequency band. The antenna’s ability to operate as either a transmitter or receiver in this particular frequency band was verified through a series of wireless transmission experiments.
The Latest on: Smart antenna
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Smart antenna” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Smart antenna
- TicWatch Pro 5 Enduro hands-on: an impressive GPS smartwatch with a cloudy futureon May 9, 2024 at 4:02 am
The best tech tutorials and in-depth reviews Issues delivered straight to your door or device When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
- WiiM unveils two new music streaming hubs for audiophiles on a budget at High End Munich 2024on May 9, 2024 at 2:00 am
Forget Sonos, WiiM just unveiled its Ultra and Amp Pro music streaming add-ons to bring multiroom audio and streaming smarts to Hi-Fi setups on a budget.
- Trimble Launches R780 GNSS Smart Antennaon May 7, 2024 at 11:20 am
Designed for construction surveyors, the R780 GNNS Smart Antenna offers performance in challenging GNSS environments, such as blocked sky, multi-path or degraded signal conditions.
- How GNSS antennas can increase farming accuracyon May 7, 2024 at 1:53 am
GNSS antennas play a crucial role in precision agriculture and are responsible for the reception of highly accurate location data, facilitating a more ...
- Embedded Antenna Systems Market Assessment: Understanding Demand and Supply Dynamicson May 6, 2024 at 10:53 pm
Embedded antennas are unique kinds of antennas to improve the performance of miniaturized antenna systems. These antennas’ principal objective is to transmit energy into space. The metamaterial ...
- Revolutionizing Connectivity: New Programmable Antenna Sets the Stage for 6G Advancementson May 2, 2024 at 6:45 am
With 5G nearing its waning phase, 6G could be next to bring high-speed data transmission, leading to holograms and uninterrupted communications.
- Breakthrough 6G antenna could lead to high-speed communications and hologramson May 2, 2024 at 4:01 am
Scientists build the world's first 6G antenna that, when fitted into devices, can transmit data at high speeds.
- Leica Geosystems launches its first Machine Smart Antenna — the Leica iCON gps 120on April 26, 2024 at 6:48 am
Leica Geosystems launches its first Machine Smart Antenna — the Leica iCON gps 120. Rating 1 2 3 4 5; Heerbrugg, Switzerland) Leica Geosystems, part of Hexagon, ...
- Adant Technologies Introduces sMART-4-mesh: A Breakthrough in Cost-Efficient and Eco-Friendly Mesh Wi-Fi Networkson April 5, 2024 at 2:10 am
By integrating Adant’s sMART-2 smart antenna technology with a dedicated machine learning software algorithm, sMART-4-mesh achieves eco-friendly operation without sacrificing reliability.
- Chapter 15: Smart Antennason March 31, 2018 at 1:15 pm
In this chapter, the smart antenna concept is introduced. The smart antenna is an emerging technology that can be used to tackle the capacity, quality, and coverage problems faced by wireless ...
via Bing News