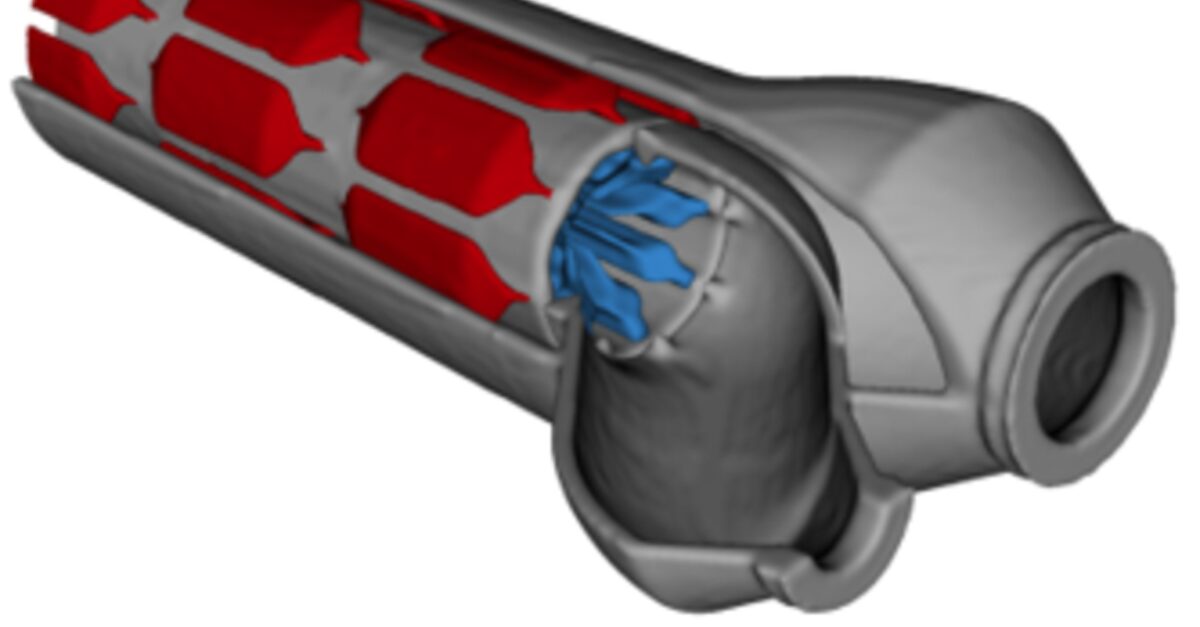
Computer Tomography (CT) X-ray image of the tube-in-tube heat exchanger. Color indicates whether hot fluid (red) in the outer tube or cold fluid (blue) in the inner tube.
Credit: Hyunkyu Moon, Davis McGregor, Nenad Miljkovic and William P. King.
Demonstrating next-generation energy technology, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign are using topology optimization and metal 3D printing to design ultra-compact, high-power heat exchangers.
Used in most major industries – including energy, water, manufacturing, transportation, construction, electronic, chemical, petrochemical, agriculture and aerospace – heat exchangers transfer thermal energy from one medium to another.
For decades, heat exchanger designs have remained relatively unchanged. Recent advancements in 3D printing allow the production of three-dimensional exchanger designs previously thought impossible. These new and innovative designs operate significantly more effectively and efficiently but require specific software tools and design methods to manufacture the high-performance devices.
Recognizing the need to unlock new, high-performing heat exchangers, Grainger College of Engineering researchers have developed software tools that enable new 3D heat exchanger designs.
“We developed shape optimization software to design a high-performance heat exchanger,” said William King, professor of Mechanical Science and Engineering at The Grainger College of Engineering and co-study leader. “The software allows us to identity 3D designs that are significantly different and better than conventional designs.”
The team started by studying a type of exchanger known as a tube-in-tube heat exchanger – where one tube is nested inside another tube. Tube-in-tube heat exchangers are commonly used in drinking water and building energy systems. Using a combination of the shape optimization software and additive manufacturing, the researchers designed fins (only made possible using metal 3D printing) internal to the tubes.
“We designed, fabricated and tested an optimized tube-in-tube heat exchanger,” said Nenad Miljkovic, associate professor of Mechanical Science and Engineering and co-study leader. “Our optimized heat exchanger has about 20 times higher volumetric power density than a current state-of-the-art commercial tube-in-tube device.”
With billions of heat exchangers in use worldwide today and even more attention placed on our need to reduce fossil fuel consumption, compact and efficient heat exchangers are increasing in demand, particularly in industries where heat exchanger size and mass significantly impacts performance, range and costs.
Original Article: Illinois researchers demonstrate extreme heat exchanger with additive manufacturing
More from: University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
3D printed heat exchanger
- Portal Space Systems comes out of stealth with satellites that’ll be fired up by the sunon April 30, 2024 at 6:00 am
Portal Space Systems is emerging from stealth with a plan to create a satellite platform that uses the sun's heat to spark its thrusters.
- Cornell University Utilizes Pigs, Mussels, and 3D Printing to Maintain Lake Source Cooling Systemon April 24, 2024 at 10:10 pm
Mark Tarazi ’24 crunched over the gravel at Ithaca’s East Shore Park marina with the new stack of 3D-printed shackle-alignment tabs.Out in Cayuga Lake, 250 feet down, there was an octagonal 4-ton scre ...
- Cost-effective nanorod electrodes for molecular hydrogen productionon April 18, 2024 at 5:00 pm
3D-printed, nickel-based electrocatalysts enable highly efficient hydrogen evolution Aug 12, 2022 Discovery enables cost-effective and eco-friendly green hydrogen production ...
- Biodegradable aerogel: Airy cellulose from a 3D printeron April 3, 2024 at 5:00 pm
3D printing can produce complex structures without waste, and ultra-light aerogels are excellent heat insulators. The material was created under the leadership of Deeptanshu Sivaraman, Wim Malfait ...
- Sajjad Bighamon May 17, 2023 at 7:56 am
He is the director of the Energy-X Lab (Energy eXploration Laboratory). Dr. Bigham is a heat transfer and energy systems specialist interested in scientific and engineering challenges that lay at the ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
3D printed heat exchanger
[google_news title=”” keyword=”3D printed heat exchanger” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Heat exchanger
- Celtics advance to East semifinals, beating short-handed Heat 118-84 in Game 5on May 1, 2024 at 7:21 pm
BOSTON (AP) — Jaylen Brown and Derrick White each scored 25 points and the Boston Celtics advanced to the Eastern Conference semifinals, beating the short-handed Miami Heat 118-84 in Game 5 on ...
- Top Plays from Boston Celtics vs. Miami Heaton May 1, 2024 at 7:20 pm
Top Plays from Boston Celtics vs. Miami Heat,05/01/2024 1.
- How to Heat Tortillas, Whether Homemade or Store-Boughton May 1, 2024 at 3:24 pm
Follow these easy methods for tender, pliable corn and flour tortillas.
- Heat networks are investment opportunity ‘worth billions’ – energy company bosson May 1, 2024 at 10:59 am
Installing heat networks to replace home gas boilers in urban areas is an investment opportunity worth tens of billions of pounds, an energy company has said.Swedish state-owned firm Vattenfall said ...
- HT Materials Science's Pioneering Heat Transfer Fluid, Maxwell™, Wins 2024 Green Product Awardon May 1, 2024 at 5:32 am
HT Materials Science (HTMS), the sustainable materials technology company based in Ireland with operations in Italy and the USA, was awarded the Green Product Award 2024 for their proprietary heat ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Heat exchanger
[google_news title=”” keyword=”heat exchanger” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]









